How to Stop Alopecia Areata From Spreading
What is Alopecia Areata?
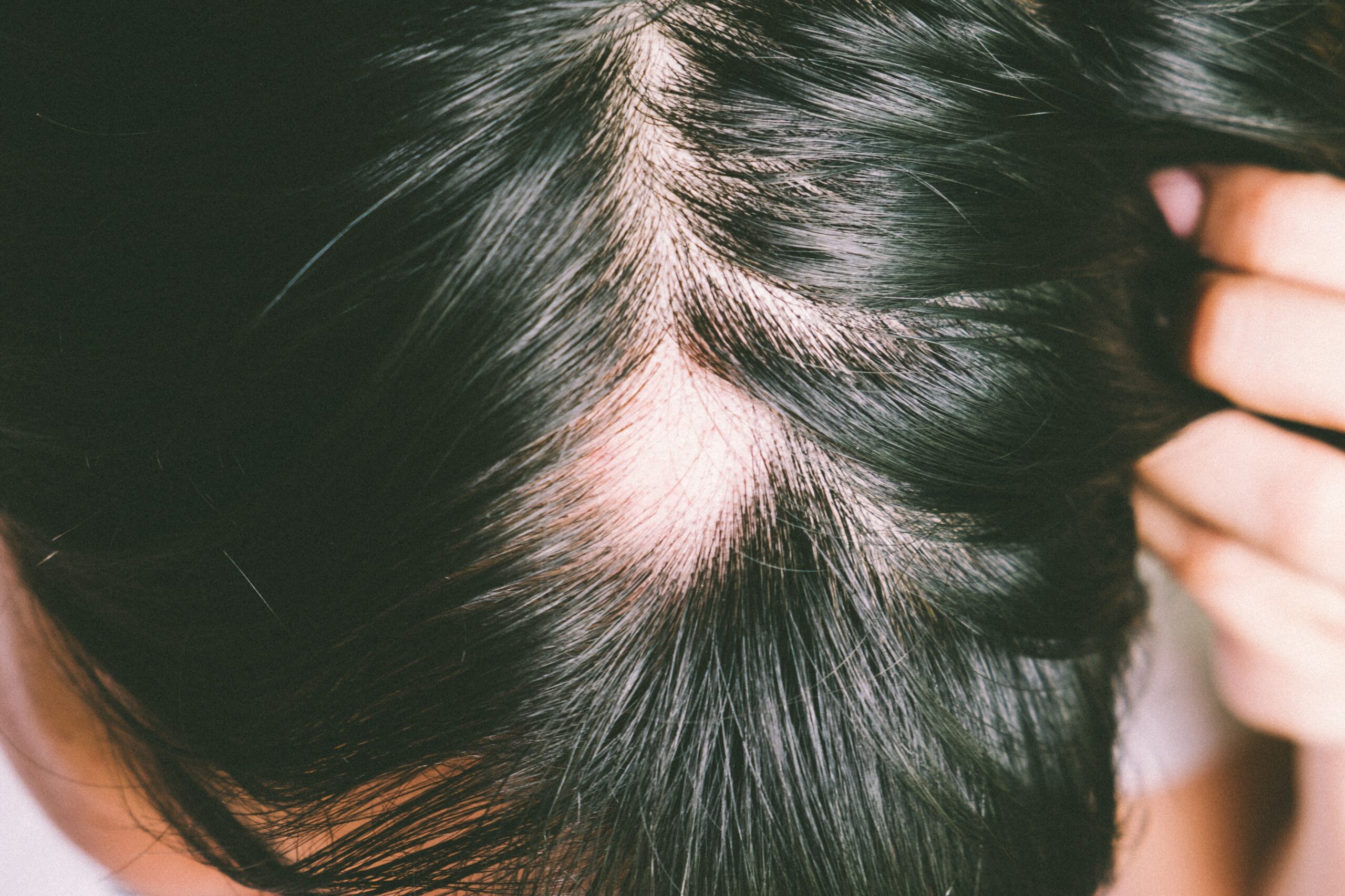
Alopecia areata is a condition that causes hair loss. It can affect men, women, and children of any age. The hair loss usually appears as one or more bald patches on the scalp. In some cases, it can also lead to complete hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or total body hair loss (alopecia universalis).
You should visit a Newport Beach hair restoration doctor for proper treatment if you are experiencing hair loss.
Types of Alopecia
The disease of alopecia comes in various forms. Alopecia areata is the most common type of alopecia since it is the most common. However, there are also other types like:
- Diffuse alopecia areata: sudden hair thinning instead of lost hair patches.
- Alopecia areata totalis: total hair loss on the head.
- Ophiasis alopecia areata: Hair loss across the back and sides of your head in a band
Causes of Alopecia Areata

Causes of Alopecia Areata in Newport Beach, California at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, the structures from which hair grows. The exact cause of alopecia areata is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Autoimmune response: The prevailing theory suggests that alopecia areata is primarily an autoimmune disorder. Usually, the immune system protects the body from foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. However, in people with alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly identifies hair follicles as foreign and attacks them. This inflammatory response disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, leading to hair loss.
- Genetic predisposition: There appears to be a genetic component to alopecia areata. Individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. Specific genetic markers related to immune system regulation and susceptibility to autoimmune diseases may increase the risk of alopecia areata.
- Triggers: While the exact trigger remains unknown, certain environmental factors and events may trigger alopecia areata in susceptible individuals. These triggers could include physical or emotional stress, illnesses, hormonal changes, certain medications, and trauma.
- Immune system dysfunction: Abnormalities in the immune system, such as an overactive immune response, could contribute to the development of alopecia areata. This dysfunction can lead to the immune cells attacking the body’s tissues, including hair follicles.
- Other autoimmune conditions: People with other autoimmune diseases, such as thyroid disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, or vitiligo, may have a higher risk of developing alopecia areata, indicating a possible common underlying mechanism.
It’s important to note that alopecia areata can affect people of all ages and can manifest in different degrees of hair loss, ranging from small patches to complete baldness (alopecia totalis) or even loss of all body hair (alopecia universalis).
If you or someone you know is experiencing hair loss, it is essential to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
The following are the noticeable signs of alopecia areata:
- Hair loss in patches
- The itching and pain in the scalp
- Hyperpigmentation in bald areas
- Pitted yellow or white nails
One should be cautious of factors that might lead to hair loss. You can prevent the disease by avoiding common triggers, including severe stress, sugar-rich diets, excessive alcohol use, and smoking. Additionally, your doctor may watch for conditions like thyroid, lupus, or other autoimmune disorders. Alopecia areata has a significant risk of development in those with conditions including type 1 diabetes and arthritis.
Men may suffer from patchy hair loss in body parts like the chest, face, and scalp. Women experience more severe hair loss, which affects the scalp, brows, and eyelashes.
Given that the hair loss pattern is abrupt, it can cease between episodes and restart at any time throughout a person’s lifespan. It might cause dread in many. But don’t worry; hair loss brought on by alopecia areata is temporary. Hair growth can resume if the autoimmune condition is treated.
Understanding How Alopecia Areata Works
It’s crucial to comprehend how alopecia areata causes hair loss before figuring out how to stop the disease from spreading. Similar to how the immune system targets viruses and germs, alopecia areata causes the body’s hair follicles to be mistakenly attacked by the immune system. The hair follicles stop producing new hair as a result, and they fall out. Other alopecia areata warning signs and symptoms may include:
- Fingernail changes like dents, white patches, roughness, thinning, and splitting
- There may be slight discomfort or itching on the skin’s surface where hair loss is about to start or has already started.
- If your eyelashes and eyebrows are lost, eye irritation or sinus discomfort may result.

Best Practices for Reducing Hair Loss Anxiety in Newport Beach, California at Neograft Hair Restoration Orange County
Best Practices for Reducing Hair Loss Anxiety
Experiencing hair loss can be a distressing and anxiety-inducing process for many individuals. It is essential to remember that hair loss is a common issue and is often a natural part of the aging process due to various factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, stress, and medical conditions. While it’s normal to feel anxious about hair loss, several best practices can help reduce hair loss anxiety:
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you’re experiencing significant hair loss, the first step is to consult a healthcare professional or a dermatologist. They can help identify the cause of your hair loss and provide appropriate advice and treatment options.
- Educate Yourself: Learning about the causes of hair loss can help demystify the process and reduce anxiety. Understand that hair loss is a complex issue with various potential triggers.
- Avoid Self-Diagnosis: Resist the temptation to self-diagnose or rely solely on information from the internet. Getting a proper diagnosis from a qualified medical professional is essential to determine the underlying cause of your hair loss.
- Focus on Overall Health: Healthy lifestyles can positively impact hair health. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, get enough sleep, and manage stress effectively. These practices promote overall well-being, which also positively affects hair health.
- Consider Hair Care Practices: Use gentle hair care products and avoid harsh chemicals and excessive heat styling. Treat your hair gently to minimize damage and breakage.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. You can practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga or engaging in hobbies that help you relax and unwind.
Remember, hair loss anxiety is normal, and many individuals go through similar emotions. By following these best practices, you can reduce anxiety and focus on promoting overall well-being.
How Do I Know if My Alopecia Areata is Spreading?
If you have alopecia areata, you may be worried that the condition will spread and cause more hair loss. While it’s true that alopecia areata can spread, it doesn’t always happen. In fact, most people who have alopecia areata only lose the hair on their scalp. only a small percentage of people with alopecia areata will lose all the hair on their body, including their eyebrows, eyelashes, and pubic hair.
If you have alopecia areata and you notice that your hair is thinning or falling out in other areas, it’s important to see a Newport Beach hair transplant doctor right away. A doctor can determine if your alopecia areata is spreading and offer treatment options to help prevent further hair loss.
Can Anything Help Slow the Spread of Alopecia Areata?
There is no sure way to prevent alopecia areata from spreading. However, there are treatments that can help stop the progression of hair loss and even regrow hair.
If you have alopecia areata, your Orange County hair restoration doctor may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
Topical corticosteroids. These are drugs that reduce inflammation. They are usually the first line of treatment for alopecia areata. Corticosteroids can be applied to the skin as a cream, lotion, foam, or ointment. They can also be injected into the affected areas of the scalp. Most people with alopecia areata will see new hair growth within six to eight weeks after starting treatment with a topical topical corticosteroid.
Oral corticosteroids. These are drugs that reduce inflammation throughout the body. They are typically used only for a short period of time because they can have serious side effects, such as high blood pressure, bone loss, and an increased risk of infection.
Minoxidil (Rogaine). This is a topical medication that is available over the counter. It is applied to the scalp twice a day. Minoxidil can also be used to treat other forms of hair loss, such as female pattern baldness.
Steroids. These are drugs that can be taken orally, injected into the skin, or applied topically. Steroids can help to stop the immune system from attacking the hair follicles. They can also help to promote hair growth.
Anthralin (Drithocreme). This is a topical medication that is available by prescription only. Anthralin is applied to the scalp once or twice a day and should be left on for several hours before being washed off.
These are just a few of the treatments that are available for alopecia areata. Your doctor can help you to decide which treatment is right for you.
In addition to medical treatments, there are a few things that you can do at home to help manage your alopecia areata.
Wear a hat or scarf when you go outside. This will help to protect your scalp from the sun and wind.
Avoid harsh hair treatments. This includes hot oil treatments, perms, and hair colorings. These can make your hair fall out more easily.
Use a soft brush on your hair. Don’t use a comb or anything else that could scratch your scalp.
Don’t pull on your hair or play with it excessively. This can cause more hair loss.
Try to reduce stress in your life. Stress can worsen alopecia areata.
If you have alopecia areata, it’s important to see a doctor. They can prescribe medication and provide other treatments that can help stop the hair loss from spreading.
How to Prevent Alopecia Areata from Worsening or Spreading
Your doctor will take the time to review how to treat the skin spots and prevent the condition from worsening or spreading if you are told you have alopecia areata. When seeking to stop alopecia areata from progressing, avoiding unnecessary scalp or hair trauma, lowering stress, and reviewing diet are all beneficial activities. Finding your particular trigger may require trial and error because an immune response brings on the condition, but your doctor is here to assist.
Treatments for Alopecia Areata
Patients with minor patches of alopecia areata who are older than ten years old may benefit through a variety of the following therapies:
- Corticosteroid injections into bald spots, administered as needed every four to eight weeks, are regarded as the most efficient therapy for patients with some hair loss patches. More than 80% of 127 individuals who had patchy hair loss and received corticosteroid injections recovered at least half of their hair after 12 weeks, according to one study. Steroids taken orally and administered systemically could also be a possibility.
- Minoxidil, also marketed under the name Rogaine®, may help maintain the stimulation of hair growth on the scalp, in the beard area, and the eyebrows. It needs to be used at least two or three times per day. Minoxidil is mainly thought to benefit older people.
- Topical Immunotherapy involves applying a substance such as diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE) to the scalp to trigger an allergic reaction. The goal is to stimulate the immune system and promote hair regrowth. This treatment is typically reserved for severe or widespread cases.
- Topical corticosteroids used on bald areas once or twice daily, as directed by the doctor, can also help with hair restoration, particularly in children.
- Phototherapy with ultraviolet A-1 (UVA-1) is an additional option. Dermatologists say they are a potential treatment since they can help people with alopecia areata grow more hair and reverse the condition.
The Bottom Line
You can have patchy hair loss on your scalp, beard, or other body areas if you have alopecia areata. Thankfully, there are several ways to prevent alopecia areata from getting worse and aggravating your discomfort.
Topical treatments or corticosteroid injections are frequently part of conventional therapy approaches. Topicals like minoxidil encourage new hair growth, whereas corticosteroids lower the inflammation brought on by an autoimmune disease called alopecia.
In addition to medication, you could benefit from lifestyle changes to minimize the severity of your alopecia areata and keep your symptoms from worsening.
Using sunscreen or a hat to shield areas of the skin with considerable hair loss, for example, will protect your skin against UV-related damage.
FAQs: How to Stop Alopecia Areata From Spreading
1. Is Alopecia Areata Contagious?
No, alopecia areata is not contagious. It is an autoimmune condition and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
2. Can Alopecia Areata Lead to Permanent Hair Loss?
While alopecia areata usually results in temporary hair loss, some individuals may experience permanent hair loss in severe cases, especially if the condition progresses to alopecia totalis or universalis.
3. Are There Any Natural Remedies for Alopecia Areata?
Natural approaches, such as essential oils (e.g., rosemary or peppermint oil), a balanced diet rich in vitamins, and stress-reduction techniques, may support hair health. However, they should not replace medical treatments.
4. Can Diet Impact Alopecia Areata?
Yes, a nutrient-rich diet may help manage the condition. Foods high in zinc, biotin, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids support overall hair and scalp health.
5. Is Alopecia Areata Linked to Other Health Conditions?
Yes, people with alopecia areata often have an increased risk of developing other autoimmune diseases such as vitiligo, lupus, or thyroid disorders.
6. How Does Stress Affect Alopecia Areata?
Stress does not directly cause alopecia areata but can act as a trigger in genetically predisposed individuals. Managing stress through mindfulness, therapy, or relaxation techniques may reduce flare-ups.
7. Can Children Develop Alopecia Areata?
Yes, alopecia areata can occur in children, sometimes as early as their first few years. It may manifest similarly to adult cases, with patchy hair loss, and often requires early medical intervention.
8. Does Alopecia Areata Affect Hair Texture After Regrowth?
Hair that regrows after alopecia areata may initially appear white or gray and have a different texture. Over time, the hair usually returns to its original color and texture.
9. Can Alopecia Areata Be Cured?
There is no known cure for alopecia areata, but treatments can help manage the condition and stimulate hair regrowth. Research into potential cures is ongoing.
10. Can Exercise Help Manage Alopecia Areata?
Regular exercise can improve overall health and reduce stress, which may help manage symptoms of alopecia areata. It also promotes better circulation, which could support hair health.
Let me know if you’d like more details on these topics!
Related Posts
- Hair Restoration Statistics 2023
- Do Hair Transplants Really Work?
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of A Hair Transplant?
- Do Hair Transplants Last Forever?
- What is a Neograft Hair Transplant?
- Can Dandruff Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Shampoo Cause Hair Loss?
- Beard and Facial Hair Transplants
- What’s the Difference Between Hair Shedding and Hair Loss?


Recent Comments