Identifying the Difference Between Hair Shedding and Hair Loss
Hair changes can be a source of concern for many people, whether men or women. Understanding the differences between normal hair shedding and true hair loss is key to addressing any issues early and effectively. This article provides essential information on hair health, the hair growth cycle, causes of hair thinning, common conditions like alopecia areata and traction alopecia, and practical tips for managing your scalp and hair.
Types of Hair Shedding
Hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, which includes various stages that regulate the shedding and regrowth of hair strands. On average, a person loses between 50 to 100 hairs daily as part of this normal process. The scalp contains around 100,000 hair follicles, each undergoing its own cycle of growth and rest.
One common type of shedding is telogen effluvium, where a significant amount of hair enters the resting phase (telogen) prematurely, resulting in noticeable hair thinning across the scalp. This condition often follows a triggering event, such as severe stress, illness, surgery, or nutritional deficiencies.
Other shedding can be seasonal or related to changes in lifestyle or diet and is usually temporary, with hair regrowth occurring once the underlying cause resolves.

Types of Hair Loss
Unlike shedding, true hair loss involves a more permanent reduction in hair volume and density due to damage or miniaturization of the hair follicles.
Common conditions include:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Pattern Hair Loss): A hereditary condition driven by genetics and hormonal imbalances. In men, this often results in a receding hairline or bald spots, while in women, diffuse thinning over the top of the head is common.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on the scalp and, in some cases, other areas of the body.
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by excessive tension on the hair from certain hairstyles, like tight braids or ponytails, leading to damage around the hairline and edges of the scalp.
- Anagen Effluvium: Rapid hair loss during the growth phase (anagen), often due to exposure to toxic agents like chemotherapy or other medications.
Each case may present different symptoms and requires a tailored approach for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Hair Shedding
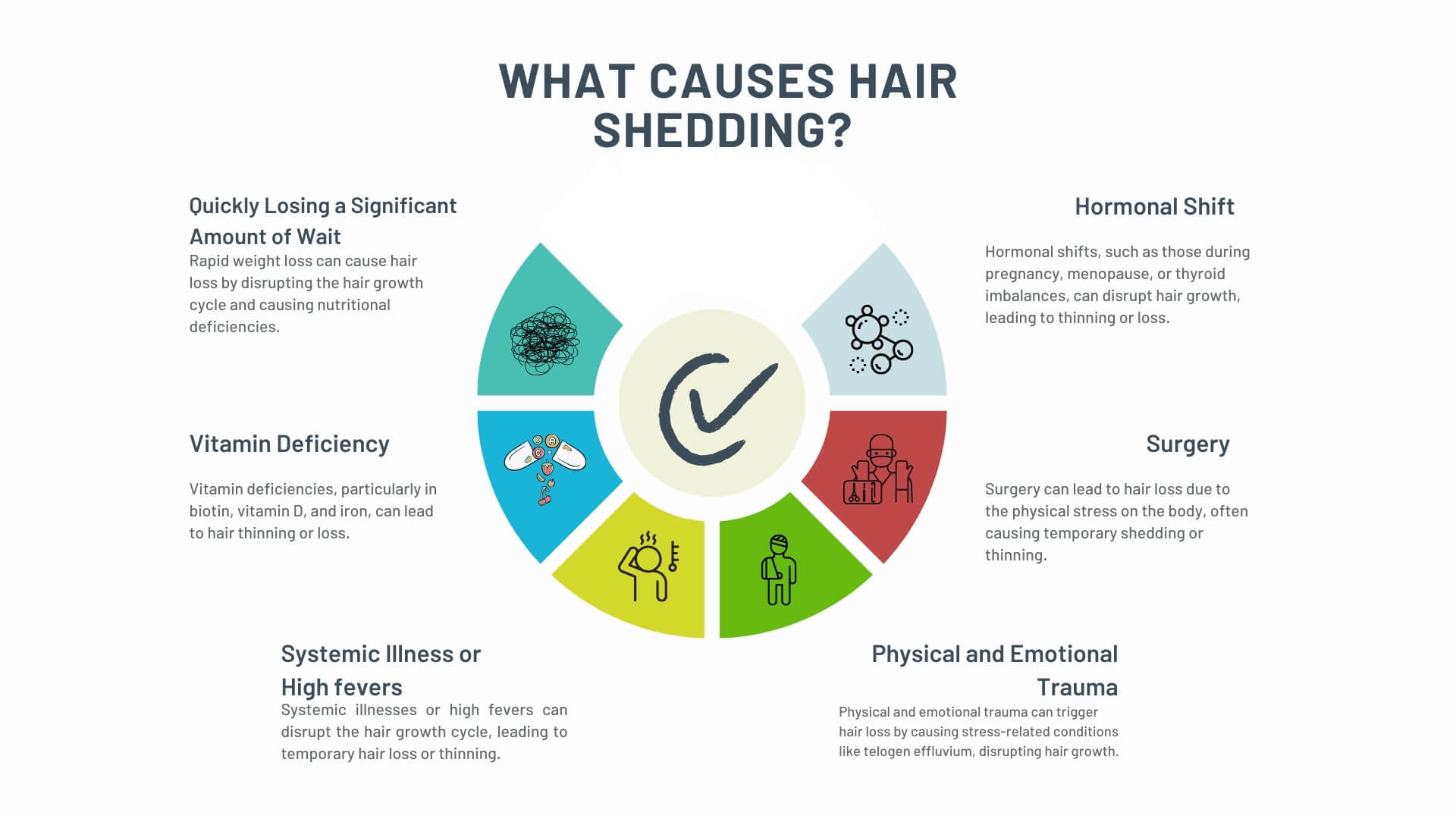
Hair shedding can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Stress: Both emotional and physical stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, pushing many hairs prematurely into the telogen phase.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Events such as pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders influence hair health.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins, minerals, and proper nutrition can impair hair growth.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antidepressants, blood thinners, and cancer treatments can cause shedding.
- Illness and Surgery: Severe illnesses or medical procedures affect the body’s balance and can lead to temporary shedding.
- Hair Care Products: Harsh ingredients in shampoos or styling products can weaken strands and irritate the scalp.
- Lifestyle Changes: Rapid weight loss, crash diets, or changes in hair care routines can also be contributing factors.
Causes of Hair Loss
Persistent hair loss is often linked to more chronic conditions or damage to the hair follicles:
- Genetics and Hormones: The most common cause is androgenetic alopecia, which depends on your genetic makeup and hormonal influences.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Diseases like alopecia areata involve the immune system attacking the follicles.
- Traction from Hairstyles: Repeated pulling or tension damages the follicles, particularly around the hairline.
- Chemotherapy and Other Medications: These disrupt the growth phase, leading to rapid hair loss.
- Skin and Scalp Conditions: Infections or inflammation of the skin can cause hair loss if untreated.
Duration and Patterns of Shedding vs. Loss
Hair shedding usually begins a few months after a triggering event and lasts for several months. The process is diffuse, affecting the entire scalp rather than specific patches or spots.
In contrast, hair loss progresses gradually, with localized thinning or bald spots developing over time. This can involve miniaturization of the hair follicle, where hairs become thinner and shorter before falling out.
Recognizing these patterns can help distinguish between normal shedding and an underlying condition requiring medical attention.
Effects on Hair Density
Shedding temporarily reduces the volume of hair but usually does not cause permanent changes to the scalp’s coverage. Hair typically regrows as the cycle returns to normal.
Hair loss, however, reduces hair density by damaging follicles or disrupting the growth phase, which results in thinner, weaker strands and visible thinning.
Identifying Normal vs. Abnormal Shedding
Normal shedding involves a moderate, consistent range of hair fall without significant loss of hair volume or scalp visibility.
Signs of abnormal shedding include:
- Excessive strands collected on your hand, pillow, or in the shower
- Noticeable hair thinning or changes in hair texture
- Increased hair breakage or difficulty styling due to loss of volume
- Diffuse thinning without distinct patches
If these symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a dermatologist or doctor is advised for accurate diagnosis.
Signs of Hair Loss to Watch For
Watch for these warning signs of progressive hair loss:
- Persistent thinning or bald spots
- Receding or uneven hairline
- Widening of the part or visible scalp through hair
- Hair strands becoming finer or brittle
- Changes in scalp skin condition like redness or irritation
Early detection can lead to improved outcomes with appropriate treatments.
Treatment Options for Shedding and Loss
Hair Shedding Treatments
- Improving nutrition and ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals
- Reducing stress and improving overall lifestyle
- Using gentle shampoo and hair care products free of harsh ingredients
- Protecting the scalp with sunscreen and avoiding excessive chemical or heat styling
- Topical serums to nourish the hair follicles and encourage healthy regrowth
Hair Loss Treatments
- Medications such as minoxidil or finasteride for androgenetic alopecia
- Hormonal therapies to address imbalances
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to stimulate hair follicles
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) to enhance growth phase activity
- Surgical options including hair transplant surgery for advanced cases
- Managing autoimmune or medical conditions with appropriate medicine
Each treatment plan should be tailored by a qualified dermatologist or hair specialist based on the individual’s diagnosis and symptoms.
Seeking Professional Help for Hair Shedding and Hair Loss
If you notice excessive hair shedding or persistent hair thinning, it’s essential to seek a professional evaluation to identify the underlying cause of the issue. There are several factors that can contribute to hair loss, including hormonal imbalances, genetics, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions. Dermatologists and other healthcare providers specialize in diagnosing hair and scalp problems, helping patients understand the specific factors contributing to their condition.
During an evaluation, the healthcare provider will examine affected areas of the scalp, review your medical history, and may recommend tests to rule out underlying health issues. It’s important not to ignore early signs, as timely diagnosis can make a significant difference in managing and treating hair loss. Whether the problem is temporary shedding or a more serious condition, professionals can guide you through the best ways to restore hair health and recommend appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes.
If you’ve been trying different hair care products or home remedies without success, or if you’re unsure about something related to your hair or scalp, a dermatologist’s expertise is invaluable. Don’t hesitate to start your search for professional help early—addressing hair loss promptly can improve results and boost your confidence.
Conclusion
Understanding the natural hair growth cycle and the differences between shedding and loss helps in recognizing when hair changes are normal or a cause for concern. Both men and women experience hair issues that can stem from a wide range of factors, including genetics, hormones, nutrition, and lifestyle.
There are a lot of things to consider when it comes to hair health, and reading articles on the topic can increase awareness and understanding. It’s important to remember that hair concerns aren’t just limited to adults—kids can also experience hair issues that require attention. Changes in the scalp, hair volume, or even the face area can all be signs that a factor is impacting hair health.
By paying close attention to these signs and seeking guidance from healthcare providers, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy hair and scalp. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for achieving the best possible results in hair regrowth and overall hair care.
Take Your Hair Health Into Your Own Hands
If you’re concerned about hair shedding or hair loss, don’t wait to seek help. At NeoGraft Hair Restoration Orange County, we offer a full range of advanced services designed to address various hair and scalp concerns. Our treatments include the innovative NeoGraft FUE hair transplant technique and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, both of which have been proven to support hair regrowth and improve overall hair health.
Put your hair care in the hands of experienced professionals who use the latest technology and products to deliver the best results. Make this the place where your journey to healthier hair begins. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore the treatment options tailored just for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can hair loss affect both a woman and a man?
Yes, hair loss can impact both women and men, though the patterns and causes often differ due to hormonal and genetic factors.
What is a common sign that indicates hair thinning rather than normal shedding?
A persistent reduction in hair volume or the appearance of visible bald spots is a common sign of thinning hair.
What role does the catagen phase play in hair growth?
The catagen phase is a short transitional stage where hair growth stops and the hair follicle prepares to shed the strand.
How can proper skin care affect scalp and hair health?
Good skin care maintains a healthy scalp environment, preventing inflammation and promoting strong hair follicles.
Can kids experience hair shedding or hair loss?
Yes, kids can experience hair shedding or hair loss, though it’s less common than in adults. For example, conditions like alopecia areata or nutritional deficiencies can cause noticeable hair thinning in children. Early evaluation by a healthcare provider is crucial for identifying the root cause and initiating appropriate treatment.
What are some effective tips to reduce hair breakage during daily hair care?
Using mild shampoos, avoiding harsh styling, and carefully detangling with a wide-tooth brush can minimize breakage.
How important is awareness about different hair loss causes?
Increased awareness helps people recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment to prevent further loss.
What should a patient expect during a consultation for hair loss?
A patient can expect a thorough scalp examination, discussion of lifestyle and health factors, and personalized treatment recommendations.
Are there medication options to treat hair loss?
Yes, there are FDA-approved medications such as minoxidil and finasteride that can slow hair loss and promote regrowth in many patients.
Can biotin supplements help with hair thinning?
Biotin may support hair health in people with deficiencies, but its effectiveness varies and should be part of a balanced diet and overall self-care.
Related Posts
- Hair Restoration Statistics 2023
- Do Hair Transplants Really Work?
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of A Hair Transplant?
- Do Hair Transplants Last Forever?
- How to Stop Alopecia Areata From Spreading
- Can Dandruff Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Shampoo Cause Hair Loss?
- Beard and Facial Hair Transplants
- What is a Neograft Hair Transplant?